
In the professional world of Cybersecurity and Digital Forensics, password strength testing is a critical task. Hashcat stands out as the world’s fastest and most versatile password recovery utility. Unlike other tools, Hashcat leverages the massive parallel processing power of modern GPUs to crack even the most complex hashes in record time.
This guide will walk you through the full setup, attack strategies, and hardware optimization techniques needed to master Hashcat on Kali Linux.
What is Hashcat?
Hashcat is an advanced, open-source password recovery tool that supports over 300 different hashing algorithms, including MD5, SHA-1, NTLM, bcrypt, and WPA/WPA2. It is the industry standard for penetration testers because of its unique ability to offload processing to the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
Quick Reference: Attack Modes & Hash Types
Understanding the command structure is essential. The basic syntax is:
hashcat -m [hash_mode] -a [attack_mode] [hash_file] [wordlist/mask]
Attack Modes (-a)
| Mode | Description | Best For |
| 0 | Straight / Dictionary | Common passwords (RockYou) |
| 1 | Combination | Combining two wordlists |
| 3 | Mask (Brute Force) | Specific patterns (e.g., Year+Name) |
| 6 | Hybrid (Wordlist + Mask) | Words followed by numbers |
Common Hash Types (-m)
| Hash Type | Mode (-m) | Common Usage |
| MD5 | 0 | Legacy CMS, older databases |
| SHA-1 | 100 | Digital signatures, Git |
| NTLM | 1000 | Windows / Active Directory environments |
| bcrypt | 3200 | Modern web apps (PHP, Django) |
| WPA2 (PBKDF2) | 22000 | Wi-Fi network security auditing |
To know the type of hash we are dealing with, we can use the hash-identifier command.
Step 1: Installing Hashcat on Kali
Most Kali Linux installations include Hashcat by default. To update it and verify your hardware, run:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install hashcat -yStep 2: Running a Dictionary Attack (Mode 0)
The dictionary attack is the most effective way to crack common passwords using lists like rockyou.txt.
You can download the rockyou.txt here.
Handling Usernames in Hash Files
When dumping a database, you often encounter a file formatted as username:hash. You do not need to manually edit the file to remove the names. Hashcat can ignore the username and focus on the hash using the --user flag.
Imagine we managed to dump this file:
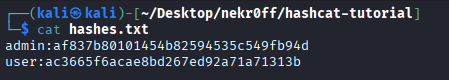
We identify is a MD5 hash, so we could execute the following command:
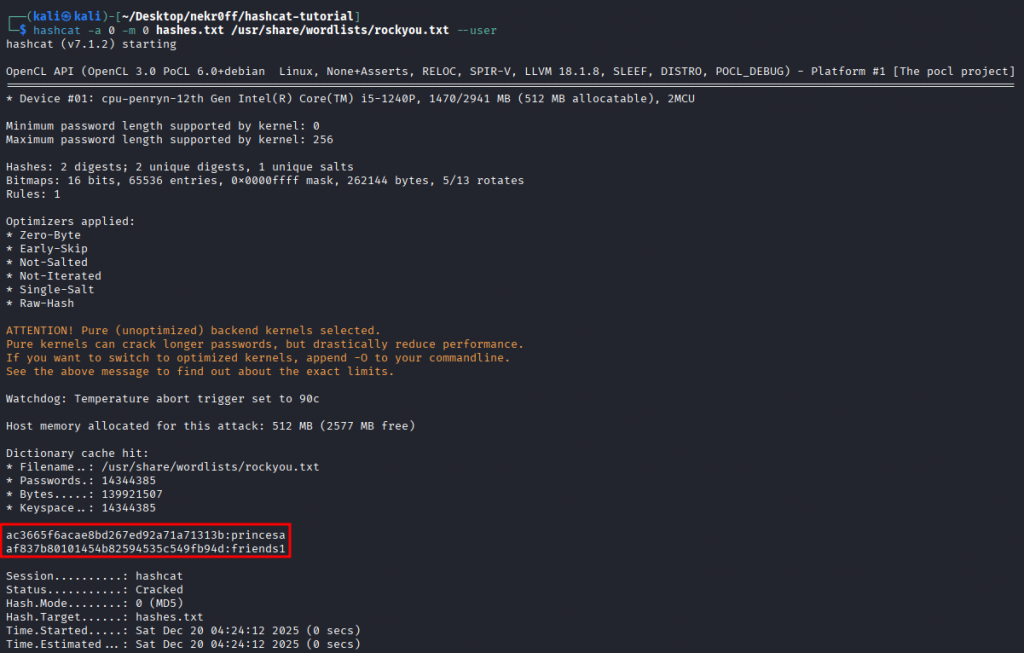
hashcat -a 0 -m 0 hashes.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --user-a 0: Sets the attack type to dictionary-m 0: Sets the hash type to MD5.-user: Tells Hashcat to ignore the text before the first colon in each line.
Obtaining the password cracked:
Step 3: Mastering Mask Attacks (Mode 3)
When wordlists fail, Mask Attacks allow you to perform brute force by defining specific patterns.
Placeholders Cheatsheet:
?u= Upercase?l= Lowecase?d= Digit?s= Special character?a= All characters (Upper + Lower + Digits + Special)
Knowing the Password Format
If we know that the password policy of the database we dumped is 3 letters and 3 numbers, we could use the following command in order to try with all password combination of 3 letters and 3 numbers:
hashcat -a 3 -m 0 hashes.txt ?l?l?l?d?d?d-a 3: Sets the attack mode to Mask Attack-m 0: Sets the hash type to MD5?l?l?l?d?d?d: Sets that the pattern of the password is 3 lower case letters and 3 digits
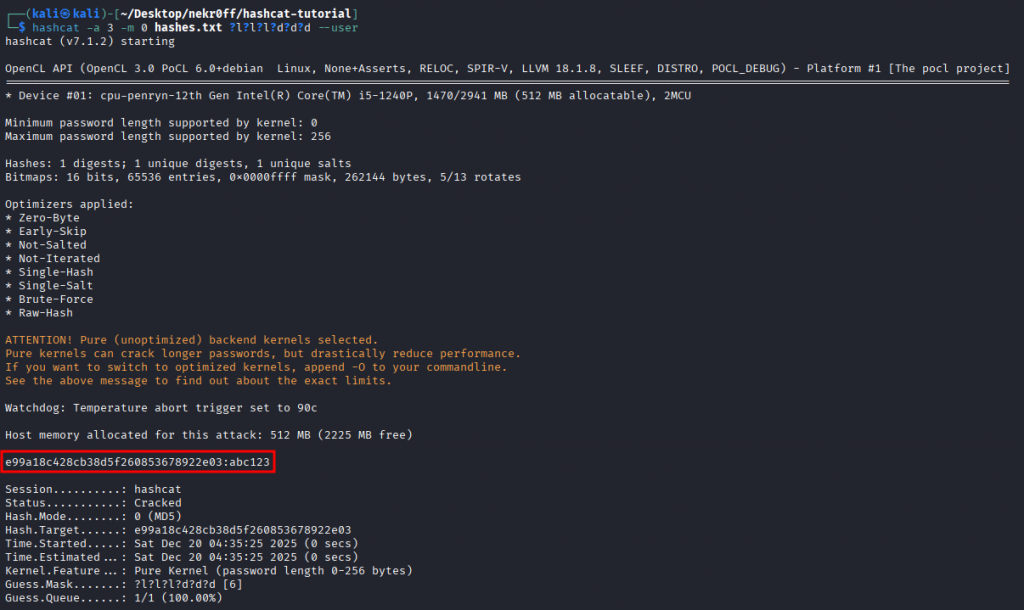
Not Knowing the Password Format
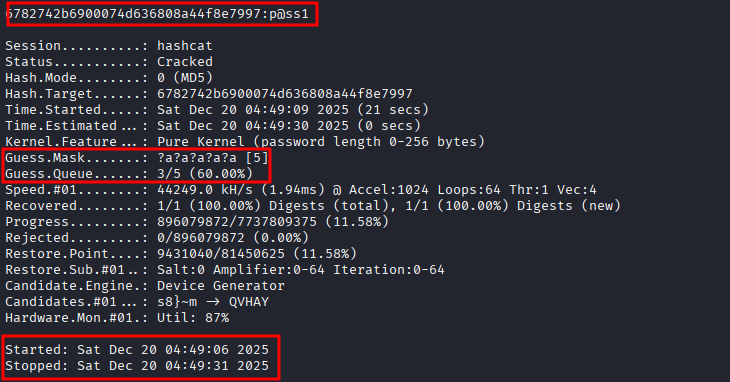
If we don’t know the length or the format of the password, we could try an incremental bruteforce attack, where we set the flag ‐‐increment and a pattern of ?a.
hashcat -a 3 -m 0 hashes.txt --increment --increment-min 3 --increment-max 7 ?a?a?a?a?a?a?a --user-a 3: Sets the attack mode to Mask Attack.-m 0: Sets the hash type to MD5.--increment,--increment-min 3,--increment-max 7: Says to hashcat that it has to increment the number of characters of the pattern, starting with 3 characters and stablishing the limit to 7 characters.?a?a?a?a?a?a?a: Sets the max pattern.--user: Says to hashcat that the file has the formatuser:hash.
Waiting a while, it will crack the password:
The Science of Security: Entropy Theory
Why do we use these attacks? It all comes down to Entropy, which measures the unpredictability of a password. A high entropy score means a password is exponentially harder to crack.
The mathematical formula for entropy is:
Where:
- E: Entropy in bits.
- L: Length of the password.
- R: Size of the character pool.
Conclusion
At this point we can conclude 2 things:
- The security of your password doesn’t rely on how much special characters it has (as we have show before), but in how long it is.
- There are some encryption methods, such as MD5, that are not safe an easy crackeable.
If you have any question, don’t doubt on contacting me to my LinkedIn.
